MySQL基本介绍与安装
浅小兮MySQL 基本介绍
MySQL模型:层次性,网状型,关系型。
数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织、存储和管理数据的仓库。
RDBMS:关系型数据库管理系统。
四大基本数据类型:<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">整型</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">浮点型</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">字符型</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">日期时间类型</font>
MySQL 安装
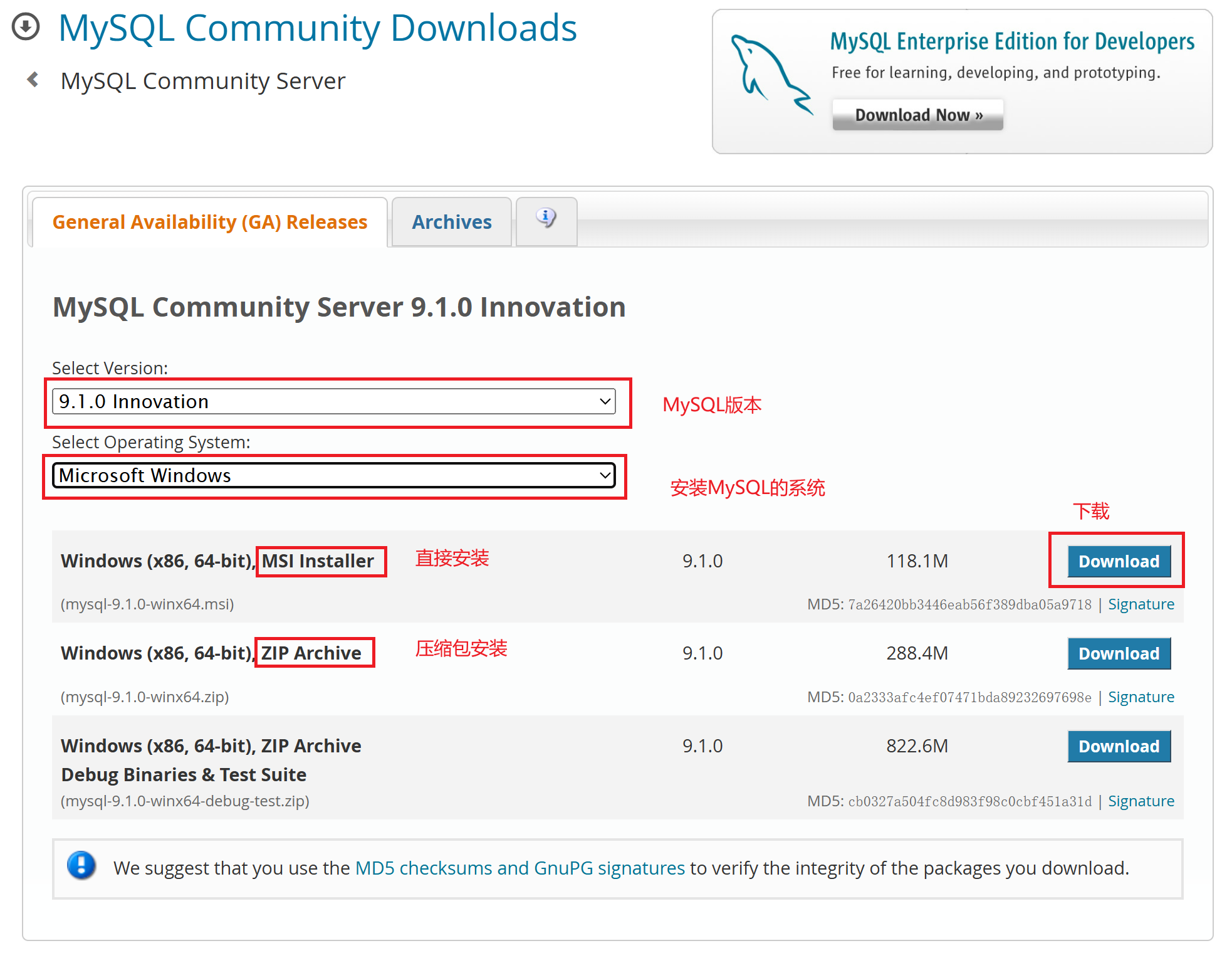
MySQL 下载地址为: MySQL 下载 。 安装需要开启管理员权限。
Linux上安装MySQL
windows系统上安装MySQL
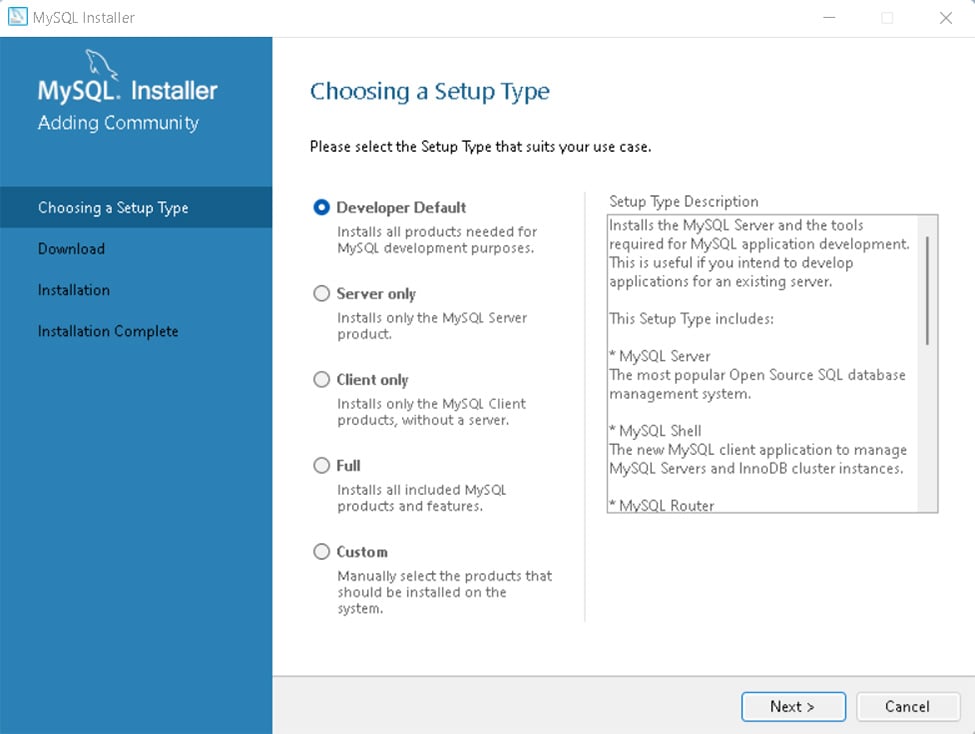
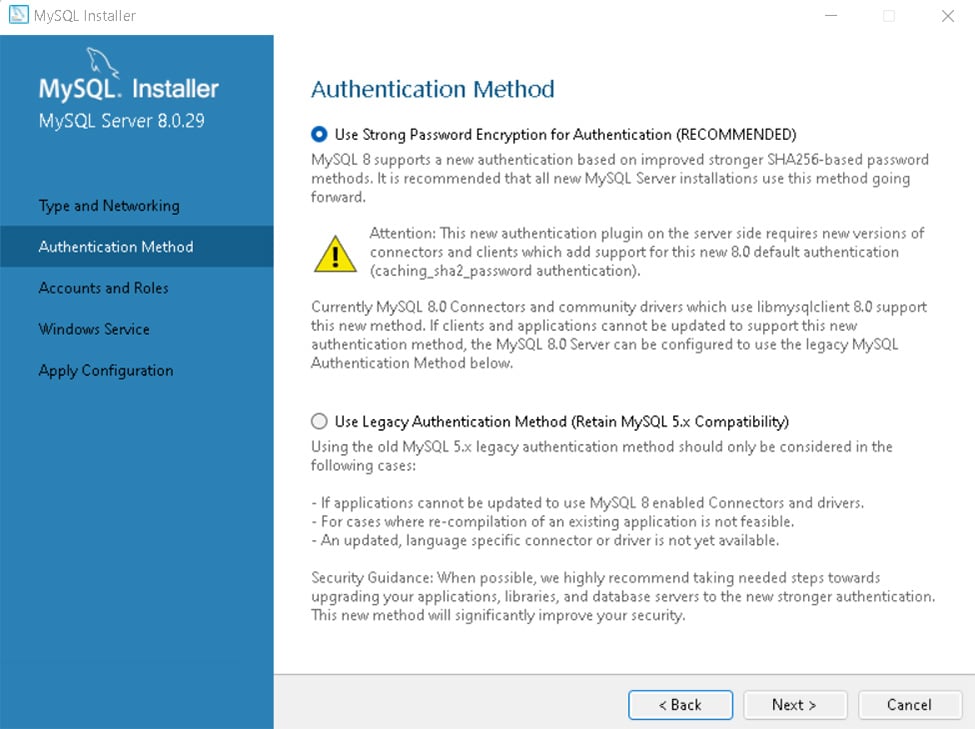
下载msi installer格式的文件后直接安装(差不多一直next就像)
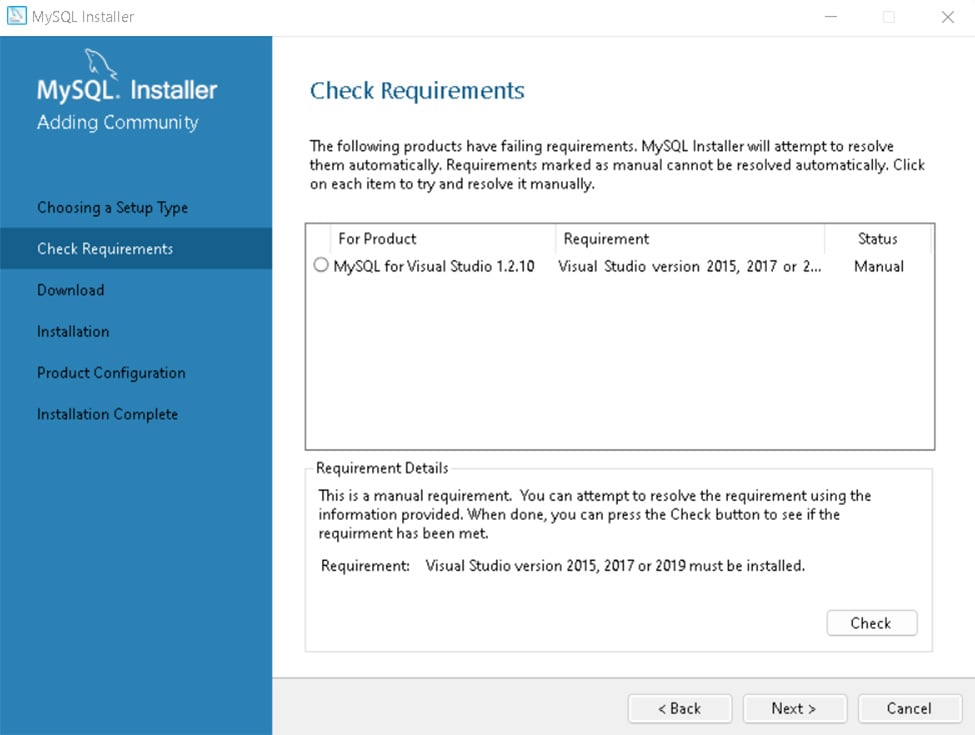
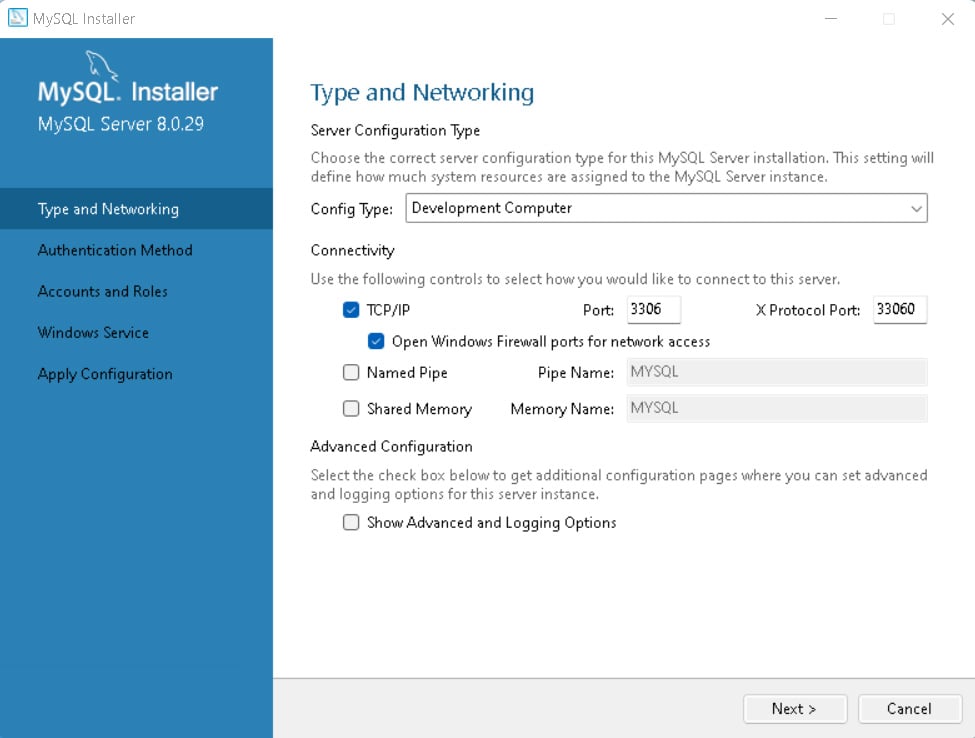
省略一部分大部分都是next
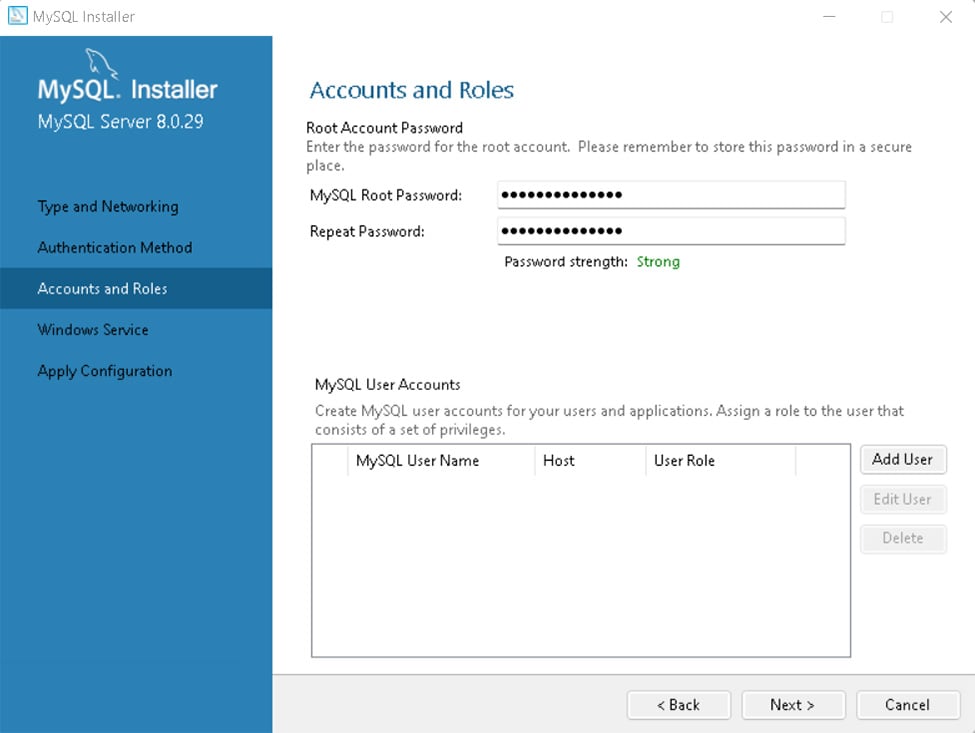
这里设置root账户密码
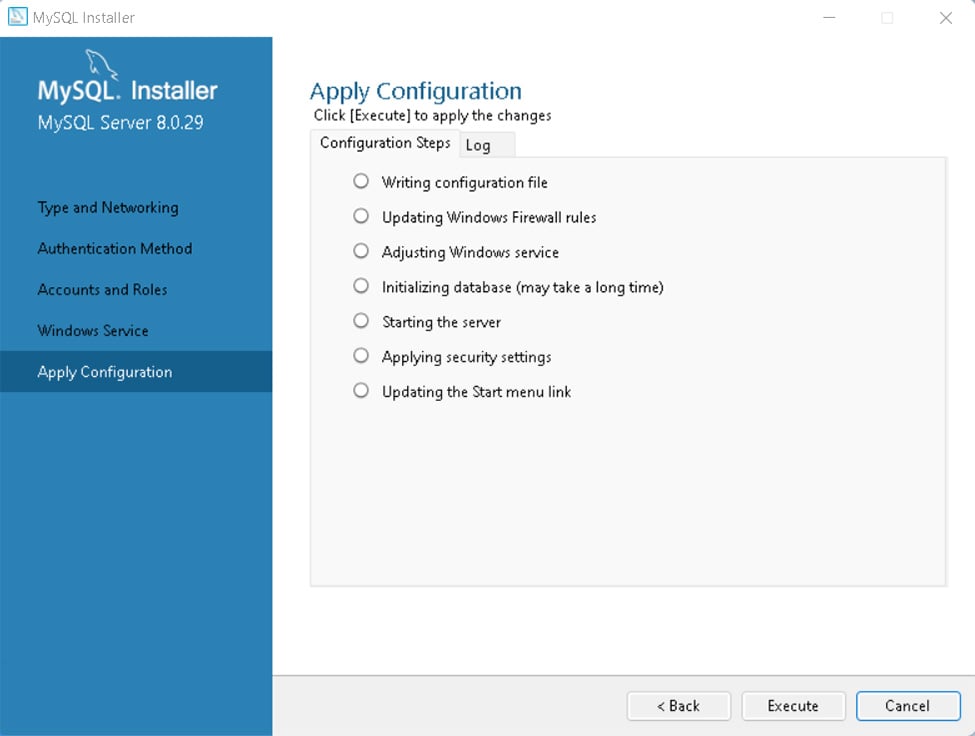
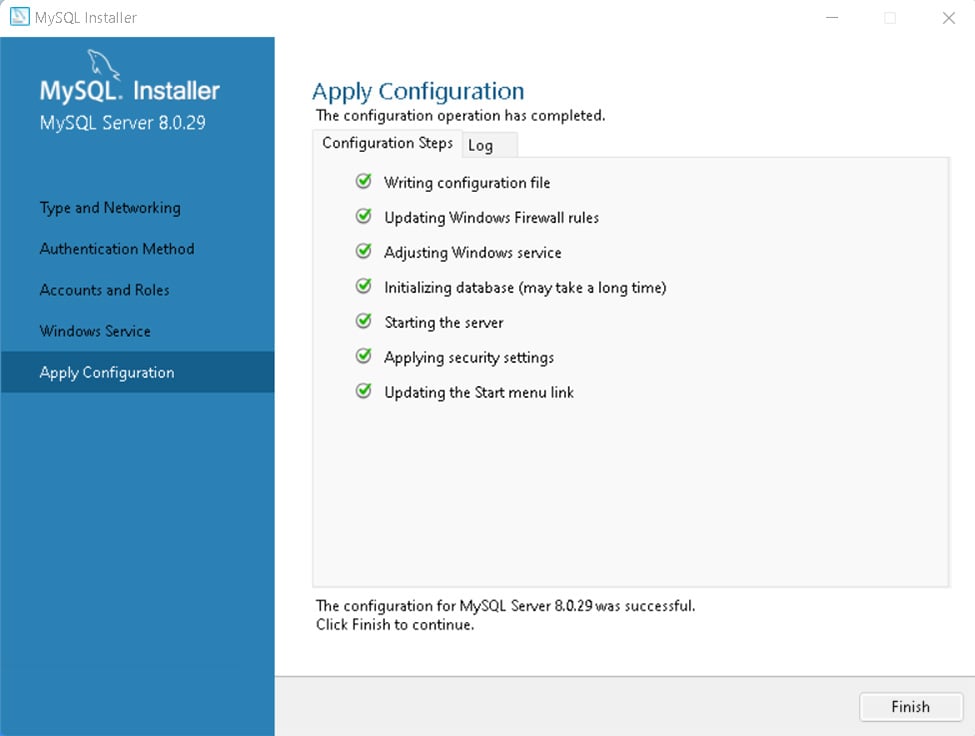
点击Execute等待下载完成
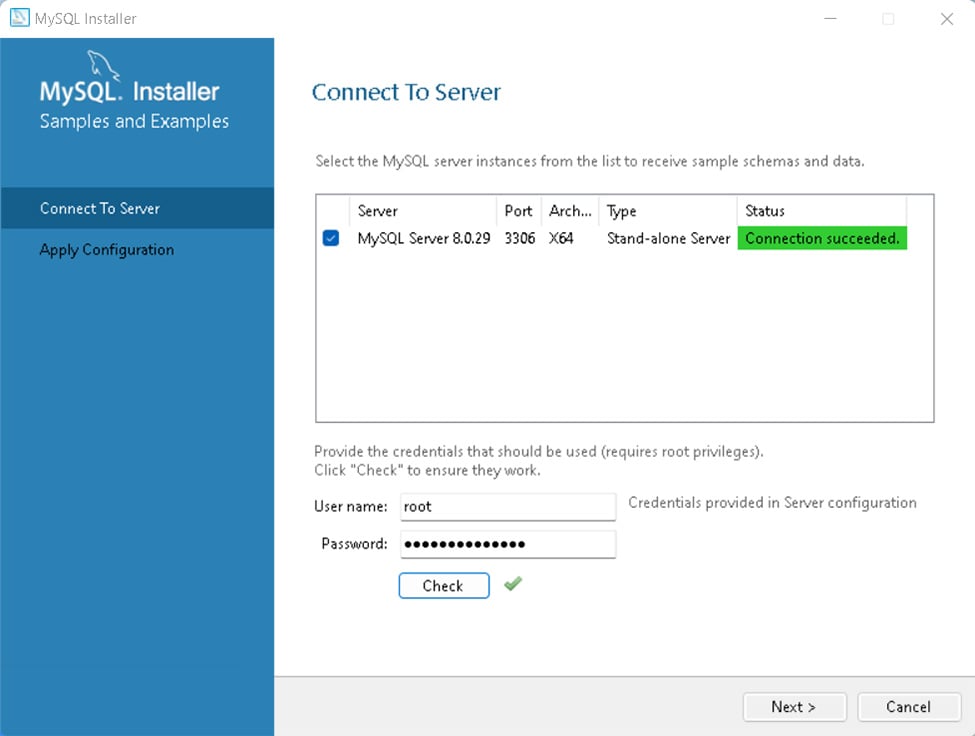
输入 root 帐户的密码,然后单击“检查”。您将看到连接成功状态:
Mac OS系统上安装MySQL
暂时没有使用该系统,未来补上。。。。。。
MySQL 管理
启动及关闭 MySQL 服务器
查看版本:
-
没有登陆mysql:mysql -V
-
登陆成功时会提示当前数据库的版本
-
登录到mysql之后:select version();
Windows 系统下
启动 MySQL 服务器:
-
通过 “服务” 管理工具: 打开"运行"对话框(Win + R),输入
**<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">services.msc</font>**,找到"MySQL"服务,右击选择"启动"。 -
通过命令提示符: 打开命令提示符(以管理员身份),输入以下命令:
1 | net start mysql |
关闭MySQL服务器:
-
通过 “服务” 管理工具:同样打开"运行"对话框,输入 services.msc,找到 “MySQL” 服务,右击选择"停止"。
-
通过命令提示符: 打开命令提示符(以管理员身份),输入以下命令:
1 | net stop mysql |
Linux 系统下
1、启动 MySQL 服务:
使用 **<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);background-color:rgb(236, 234, 230);">systemd</font>**命令(适用于大多数现代 Linux 发行版,如 Ubuntu、CentOS 等):
1 | sudo systemctl start mysql |
使用**<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">service</font>**命令(在一些较旧的发行版中):
1 | sudo service mysql start |
2、关闭 MySQL 服务:
使用 systemd:
1 | sudo systemctl stop mysql |
使用 service 命令:
1 | sudo service mysql stop |
3、重启 MySQL 服务:
使用 systemd:
1 | sudo systemctl restart mysql |
使用 service 命令:
1 | sudo service mysql restart |
4、检查 MySQL 服务状态:
使用 systemd命令:
1 | sudo systemctl status mysql |
使用 service 命令:
1 | sudo service mysql status |
MySQL 用户设置
在 MySQL 中,用户设置包括创建用户、设置权限、管理用户等操作。以下是一些常用的 MySQL 用户设置操作,包括创建用户、设置权限、查看和删除用户等。
创建用户
sql命令:
1 | CREATE USER 'username'@'host' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; |
-
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">username</font>:用户名。 -
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">host</font>:指定用户可以从哪些主机连接。例如,<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">localhost</font>仅允许本地连接,<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">%</font>允许从任何主机连接。 -
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">password</font>:用户的密码。
授权权限
创建用户后,你需要授予他们访问权限,使用 GRANT 命令来授予权限:
1 | GRANT privileges ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'host'; |
-
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">privileges</font>:所需的权限,如<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">ALL PRIVILEGES</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">SELECT</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">INSERT</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">UPDATE</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">DELETE</font>等。 -
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">database_name.*</font>:表示对某个数据库或表授予权限。<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">database_name.*</font>表示对整个数据库的所有表授予权限,<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">database_name.table_name</font>表示对指定的表授予权限。 -
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">TO 'username'@'host'</font>:指定授予权限的用户和主机。
刷新权限
授予或撤销权限后,需要刷新权限使更改生效:
1 | FLUSH PRIVILEGES; |
查看用户权限
要查看特定用户的权限,可以使用以下命令:
1 | SHOW GRANTS FOR 'username'@'host'; |
删除用户
如果需要删除用户,可以使用以下命令:
1 | DROP USER 'username'@'host'; |
修改用户密码
要修改用户的密码,可以使用 ALTER USER 命令:
1 | ALTER USER 'username'@'host' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password'; |
管理MySQL的命令
SHOW DATABASES:
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">show databases;</font>列出 MySQL 数据库管理系统的数据库列表。
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">select database();</font>查看当前所在的数据库。
USE 数据库名 :
选择或者切换操作的Mysql数据库,使用该命令后所有Mysql命令都只针对该数据库。
SHOW TABLES:
<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">show table;</font>显示指定数据库的所有表,使用该命令前需要使用 use 命令来选择要操作的数据库。
日期和时间查询:
查看当前系统日期时间: <font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">select now();</font>
查看当前系统日期:<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">select curdate();</font>
查看当前系统时间:<font style="color:rgb(51, 51, 51);">select curtime();</font>
查看表结构:desc 表名;